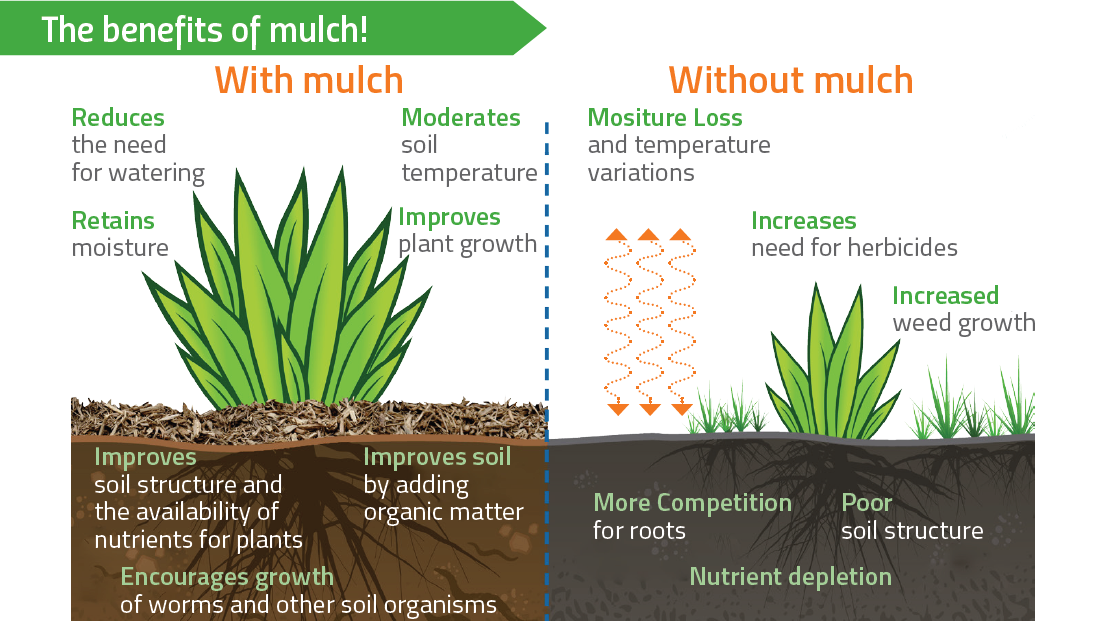
In the realm of gardening and agriculture, the use of mulch is a common practice celebrated for its multifaceted benefits. Mulch serves not only as a protective layer for soil but also plays a pivotal role in fungal suppression. Understanding the symbiotic relationship between mulch and fungal growth is essential for optimizing agricultural practices.
| Points to Consider |
|---|
| Definition of mulch |
| Importance of fungal suppression |
| Overview of mulch’s role in preventing fungal growth |
Mulch acts as a shield, safeguarding soil and plants from various environmental stressors, including fungal infections. Let’s delve into the nuances of this intricate relationship.
Types of Mulch for Fungal Suppression
Mulch comes in various forms, each offering distinct advantages in fungal suppression. Organic and inorganic mulches exhibit unique properties that influence their effectiveness against fungal growth.
| Mulch Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Organic Mulch | Derived from natural sources like wood chips, straw |
| Inorganic Mulch | Synthetic materials such as plastic, gravel |

Source Image: blog.chromascape.com
While both types serve their purpose, the choice between organic and inorganic mulches often depends on specific needs and preferences.
Mechanisms of Fungal Suppression by Mulch
Understanding how mulch combats fungal growth is crucial for harnessing its full potential. Mulch employs various mechanisms to create an inhospitable environment for fungi.
| Mechanisms | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical barriers | Mulch layers create a physical obstruction, preventing fungal spores from accessing the soil surface. |
| Moisture regulation | By regulating soil moisture levels, mulch inhibits fungal habitat formation, limiting fungal proliferation. |
| Chemical properties | Certain mulch types possess chemical compounds that actively inhibit fungal growth, acting as natural fungicides. |
These mechanisms work synergistically to suppress fungal activity, promoting healthier soil and plants.
Mulch Thickness and Fungal Suppression
Mulch thickness plays a crucial role in its efficacy against fungal growth. Finding the optimal thickness is essential for achieving maximum fungal suppression without compromising other soil properties.
| Factors to Consider | Impact on Fungal Suppression |
|---|---|
| Optimal thickness | Ensures adequate coverage to prevent fungal spore penetration. |
| Effects of varying depth | Thicker mulch layers provide greater suppression but may impede moisture regulation. |
| Balancing considerations | Striking a balance between fungal suppression and moisture retention is paramount for optimal results. |
Achieving the perfect balance is key to reaping the benefits of mulch without unintended consequences.

Source Image: tranquilurbanhomestead.com
Mulch Material Composition and Fungal Suppression
The composition of mulch materials significantly influences their ability to suppress fungal growth. Understanding the chemical constituents and decomposition rates of mulches is essential for effective fungal control.
| Material Composition | Impact on Fungal Suppression |
|---|---|
| Chemical constituents | Certain compounds within mulch actively inhibit fungal proliferation. |
| Decomposition rate | Mulches with slower decomposition rates provide longer-lasting fungal suppression. |
| Role of microbial activity | Microorganisms present in mulch contribute to fungal inhibition through various metabolic processes. |
Choosing the right mulch material is crucial for achieving desired fungal suppression outcomes.
Mulch Application Techniques for Fungal Suppression
Proper application techniques enhance the efficacy of mulch in fungal suppression. Strategic placement and timing considerations maximize its benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks.
| Application Techniques | Description |
|---|---|
| Proper mulch placement | Ensures uniform coverage and adequate depth for effective fungal suppression. |
| Mulch layering techniques | Layering different mulch materials can enhance fungal suppression properties. |
| Timing considerations | Applying mulch at opportune times, such as before fungal growth peaks, optimizes its efficacy. |
By employing these techniques, gardeners can harness the full potential of mulch in combating fungal infections.

Source Image: www.pinterest.com
Mulch and Soil Microbiology
The interaction between mulch and soil microbiota plays a crucial role in fungal suppression. Mulch fosters beneficial microbial communities that contribute to a healthier soil ecosystem.
| Interaction Dynamics | Impact on Fungal Suppression |
|---|---|
| Beneficial microbial communities | Mulch supports the growth of beneficial microbes that compete with fungi for resources, limiting their proliferation. |
| Soil pH influence | Mulch can influence soil pH levels, creating conditions unfavorable for fungal growth. |
| Soil ecology implications | Understanding the broader implications of mulch on soil ecology aids in optimizing fungal suppression strategies. |
By nurturing a diverse soil microbiome, mulch contributes to long-term fungal suppression and overall soil health.
Mulch and Plant Health
The relationship between mulch and plant health is intimately linked with fungal suppression. By preventing fungal infections, mulch promotes robust plant growth and vitality.
| Plant Health Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevention of fungal diseases | Mulch acts as a barrier, preventing fungal spores from infecting plant roots and foliage. |
| Nutrient cycling | Decomposing mulch releases nutrients into the soil, promoting plant vigor and resilience to fungal pathogens. |
| Overall plant vitality | Healthy plants are more resilient to fungal infections, making mulch an invaluable tool for maintaining plant health. |
Incorporating mulch into gardening practices is essential for fostering a thriving plant ecosystem.

Source Image: www.4glandscaping.com
Environmental Considerations of Mulch Usage for Fungal Suppression
While mulch offers numerous benefits, its usage must be mindful of environmental implications. Sustainable practices mitigate potential risks associated with mulch application.
| Environmental Considerations | Description |
|---|---|
| Sustainability practices | Using locally sourced, biodegradable mulch materials minimizes environmental impact. |
| Soil ecology preservation | Mulch should support soil biodiversity and ecosystem resilience for long-term sustainability. |
| Risk mitigation strategies | Identifying and mitigating potential environmental risks associated with mulch application ensures responsible gardening practices. |
By adopting environmentally conscious approaches, gardeners can leverage the benefits of mulch while minimizing harm to the ecosystem.
Mulch and Weed Control
In addition to fungal suppression, mulch offers secondary benefits in weed control. By limiting weed growth, mulch indirectly reduces competition for resources, further suppressing fungal proliferation.
| Weed Control Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Suppression of weed growth | Mulch physically blocks sunlight, preventing weed seeds from germinating. |
| Resource competition dynamics | Reduced weed competition alleviates stress on plants, enhancing their resilience to fungal infections. |
| Integrated weed and fungal control | Combining mulch with other control methods creates synergistic effects, maximizing overall pest management efficacy. |
By addressing both weed and fungal challenges simultaneously, mulch proves to be a versatile tool in sustainable gardening practices.
Mulch Selection Criteria for Fungal Suppression
Choosing the right mulch is essential for effective fungal suppression. Several factors, including material compatibility and cost-effectiveness, influence the selection process.
Source Image: www.bundaberg.qld.gov.au
Mulch Benefits for Fungal Suppression
By carefully evaluating these criteria, gardeners can make informed decisions when selecting mulch for fungal suppression.
Mulch Maintenance Practices for Optimal Fungal Suppression
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the continued efficacy of mulch in fungal suppression. Monitoring and timely interventions are key to mitigating fungal growth.
| Maintenance Practices | Description |
|---|---|
| Mulch replenishment frequency | Regularly replenishing mulch layers prevents fungal spores from reaching the soil surface. |
| Monitoring for fungal growth | Vigilant monitoring allows for early detection of fungal infestations, enabling prompt intervention. |
| Incorporation into soil management | Integrating mulch into soil management plans ensures long-term fungal suppression and soil health. |
By incorporating these practices into routine garden maintenance, gardeners can maximize the benefits of mulch in fungal suppression.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Mulch for Fungal Suppression
Real-world examples provide valuable insights into the practical application of mulch for fungal suppression. Case studies highlight successful strategies and best practices for achieving optimal results.
| Case Study Examples | Description |
|---|---|
| Mulch in commercial agriculture | Examining large-scale agricultural operations utilizing mulch for fungal suppression and its impact on crop yields. |
| Mulch in backyard gardening | Showcase of backyard gardeners effectively using mulch to prevent fungal diseases and promote plant health. |
| Lessons learned and best practices | Extracting valuable lessons and best practices from successful mulch implementation cases to inform future gardening endeavors. |
These case studies offer valuable lessons and inspiration for gardeners looking to harness the power of mulch in fungal suppression.

Source Image: www.stanlerfarms.co.za
Challenges and Limitations of Mulch Usage for Fungal Suppression
Despite its numerous benefits, mulch usage for fungal suppression is not without challenges and limitations. Understanding these hurdles is essential for developing effective mitigation strategies.
| Challenges and Limitations | Description |
|---|---|
| Common obstacles encountered | Identifying and addressing common challenges, such as mulch displacement and decomposition, that impact fungal suppression efficacy. |
| Limitations in fungal control | Recognizing the inherent limitations of mulch in preventing certain types of fungal diseases and developing alternative control methods. |
| Strategies for optimization | Implementing strategies to overcome challenges and optimize mulch efficacy for fungal suppression in diverse gardening environments. |
By acknowledging and proactively addressing these challenges, gardeners can maximize the effectiveness of mulch in fungal control.
Future Directions in Mulch Research for Fungal Suppression
As agricultural practices evolve, so too must mulch research. Exploring emerging technologies and interdisciplinary approaches holds the key to unlocking new frontiers in fungal suppression.
| Future Research Directions | Description |
|---|---|
| Emerging technologies | Investigating the potential of emerging technologies, such as biodegradable mulch films and genetic modification of mulch materials, for enhanced fungal suppression. |
| Interdisciplinary collaborations | Encouraging collaboration between agronomists, microbiologists, and material scientists to develop innovative mulch solutions tailored for specific fungal pathogens. |
| Addressing knowledge gaps | Identifying and addressing knowledge gaps in mulch-fungal interactions to refine existing practices and develop more effective fungal control strategies. |
By embracing these future research directions, the gardening community can stay at the forefront of fungal suppression innovation.
Mulch stands as a versatile ally in the battle against fungal infections in gardening and agriculture. By understanding its mechanisms, selecting appropriate materials, and implementing proper maintenance practices, gardeners can harness the full potential of mulch for fungal suppression. Moreover, ongoing research and collaboration promise to further refine mulch’s efficacy, ensuring a brighter, healthier future for gardens everywhere.