Are you dreaming of a lush, green lawn that turns your neighbors green with envy? The secret lies in understanding and properly using lawn fertilizers. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of lawn fertilizers, covering everything from types and benefits to application techniques and seasonal needs. So, grab your gardening gloves and let’s get started!
Importance of Fertilizing Your Lawn
Fertilizing your lawn is more than just a seasonal chore—it’s a crucial part of maintaining a healthy, vibrant lawn. Let’s explore why fertilization is so important.
Benefits of Lawn Fertilization
Fertilization helps in:
- Promoting Healthy Growth: Ensures lush and robust grass.
- Enhancing Color: Keeps your lawn looking green and vibrant.
- Strengthening Roots: Develops a deep and resilient root system.
- Weed Prevention: Thick grass crowds out weeds.
- Disease Resistance: Boosts lawn’s immunity against diseases.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Healthy Growth | Lush and robust grass |
| Enhanced Color | Keeps lawn green and vibrant |
| Stronger Roots | Develops deep and resilient root system |
| Weed Prevention | Thick grass crowds out weeds |
| Disease Resistance | Boosts lawn’s immunity against diseases |
Source Image: stewartslawn.com
Overview of Lawn Fertilizer Types
Navigating the myriad of lawn fertilizers available can be overwhelming. Understanding the basic types is the first step in making an informed choice.
Types of Lawn Fertilizers
- Organic Fertilizers: Derived from natural sources like compost and manure.
- Synthetic Fertilizers: Chemically manufactured to provide specific nutrients.
- Granular Fertilizers: Solid form, easy to apply, slow-releasing.
- Liquid Fertilizers: Quick absorption, ideal for rapid results.
- Slow-release Fertilizers: Provides nutrients gradually over time.
- Quick-release Fertilizers: Delivers nutrients immediately.
| Fertilizer Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Organic | Natural sources like compost and manure |
| Synthetic | Chemically manufactured nutrients |
| Granular | Solid form, slow-releasing |
| Liquid | Quick absorption, rapid results |
| Slow-release | Gradual nutrient delivery |
| Quick-release | Immediate nutrient delivery |
Understanding Lawn Nutrient Needs
Knowing what nutrients your lawn needs is vital for choosing the right fertilizer. Lawns primarily require three essential nutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K).
Essential Nutrients for Lawn Health
- Nitrogen (N): Promotes lush, green growth.
- Phosphorus (P): Supports root development.
- Potassium (K): Enhances overall health and disease resistance.
| Nutrient | Function |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Promotes lush, green growth |
| Phosphorus (P) | Supports root development |
| Potassium (K) | Enhances overall health and disease resistance |
Symptoms of Nutrient Deficiencies
Recognizing nutrient deficiencies can help you adjust your fertilization strategy.
- Nitrogen Deficiency: Yellowing of grass.
- Phosphorus Deficiency: Stunted growth and poor root development.
- Potassium Deficiency: Weak, thin grass, and increased susceptibility to disease.
| Deficiency | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Yellowing of grass |
| Phosphorus | Stunted growth, poor root development |
| Potassium | Weak, thin grass, susceptibility to disease |

Source Image: revivegarden.com
Soil Testing and Analysis
Before you can properly fertilize your lawn, it’s essential to understand the current state of your soil.
Importance of Soil Testing
- Nutrient Levels: Determines existing nutrient levels.
- pH Balance: Ensures soil pH is suitable for grass growth.
- Customized Fertilization: Tailors fertilizer choice to soil needs.
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Nutrient Levels | Determines existing nutrient levels |
| pH Balance | Ensures soil pH is suitable for grass growth |
| Customized Fertilization | Tailors fertilizer choice to soil needs |
Types of Lawn Fertilizers
Selecting the right fertilizer involves understanding the pros and cons of different types.
Organic vs. Synthetic Fertilizers
| Comparison | Organic | Synthetic |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural materials like compost and manure | Chemically manufactured nutrients |
| Environmental Impact | Environmentally friendly, improves soil health | Can cause runoff, potentially harmful to the environment |
| Nutrient Release | Slow, gradual release | Quick, immediate release |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Typically cheaper |
Granular vs. Liquid Fertilizers
| Comparison | Granular | Liquid |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Easy to apply, slow-releasing | Requires mixing and spraying, quick absorption |
| Nutrient Delivery | Gradual nutrient delivery | Immediate nutrient delivery |
| Convenience | Convenient for large areas | Ideal for targeted treatments |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective | Can be more expensive due to frequent applications |
Slow-release vs. Quick-release Fertilizers
| Comparison | Slow-release | Quick-release |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Release | Gradual over time | Immediate nutrient availability |
| Longevity | Fewer applications needed | More frequent applications required |
| Risk of Burn | Lower risk of burning grass | Higher risk if over-applied |
| Cost | Typically higher upfront cost | Usually cheaper initially |

Source Image: www.slideshare.net
Reading Fertilizer Labels
Understanding fertilizer labels is crucial to ensure you’re using the right product for your lawn’s needs.
Understanding N-P-K Ratios
The N-P-K ratio indicates the percentage of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium in the fertilizer.
- N (Nitrogen): Promotes leaf growth.
- P (Phosphorus): Supports root and flower development.
- K (Potassium): Enhances overall health.
| N-P-K Ratio | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Promotes leaf growth |
| Phosphorus (P) | Supports root and flower development |
| Potassium (K) | Enhances overall health |
Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients
Besides N-P-K, lawns may need secondary nutrients and micronutrients for optimal health.
- Calcium (Ca): Improves soil structure.
- Magnesium (Mg): Essential for chlorophyll production.
- Sulfur (S): Vital for protein synthesis.
- Iron (Fe): Prevents yellowing of grass.
- Manganese (Mn): Assists in enzyme processes.
| Nutrient | Function |
|---|---|
| Calcium (Ca) | Improves soil structure |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Essential for chlorophyll production |
| Sulfur (S) | Vital for protein synthesis |
| Iron (Fe) | Prevents yellowing of grass |
| Manganese (Mn) | Assists in enzyme processes |
Interpreting Application Instructions
Properly following application instructions ensures effective and safe fertilization.
- Dosage: Use the recommended amount to avoid over-fertilization.
- Frequency: Apply as often as indicated on the label.
- Method: Follow specific application methods, such as watering in granular fertilizers.
| Instruction | Importance |
|---|---|
| Dosage | Prevents over-fertilization |
| Frequency | Ensures consistent nutrient supply |
| Method | Optimizes fertilizer effectiveness |

Source Image: lawnbutler.net
Lawn Fertilizer Selection Criteria
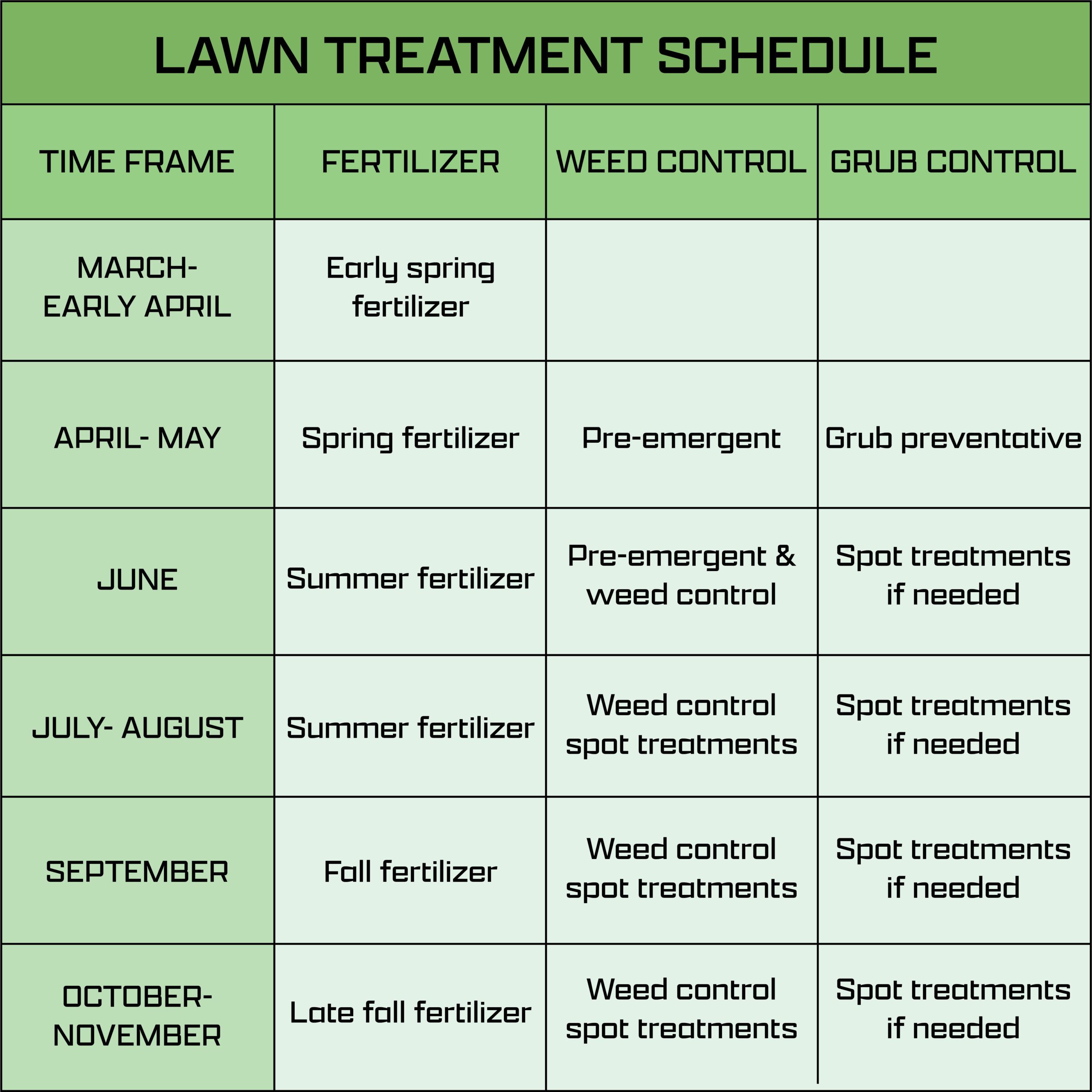
Choosing Fertilizers for Different Seasons
Your lawn’s nutrient needs change with the seasons. Here’s how to choose the right fertilizer for each season.
Spring Fertilization Needs
Spring is a time of growth and rejuvenation for your lawn.
- Nitrogen-rich fertilizers: Promote green, lush growth.
- Balanced N-P-K ratios: Support overall health.
| Season | Fertilizer Type |
|---|---|
| Spring | Nitrogen-rich, balanced N-P-K |
Summer Fertilization Strategies
Summer can be stressful for lawns due to heat and drought.
- Slow-release fertilizers: Provide steady nutrients.
- Potassium-rich formulas: Enhance drought tolerance and disease resistance.
| Season | Fertilizer Type |
|---|---|
| Summer | Slow-release, potassium-rich |
Fall and Winter Fertilization
Preparing your lawn for the colder months is crucial for its health and recovery in spring.
- Phosphorus-rich fertilizers: Encourage root development.
- Winterizer fertilizers: Strengthen grass for winter dormancy.
| Season | Fertilizer Type |
|---|---|
| Fall/Winter | Phosphorus-rich, winterizer |
Selecting Fertilizers Based on Grass Type
Different grass types have varying nutrient requirements. Let’s explore the best fertilizers for cool-season and warm-season grasses.
Cool-season Grasses
Cool-season grasses thrive in cooler climates and need specific fertilizers to stay healthy.
- High-nitrogen fertilizers: Promote growth and color.
- Balanced N-P-K ratios: Support year-round health.
| Grass Type | Fertilizer Type |
|---|---|
| Cool-season | High-nitrogen, balanced N-P-K |
Warm-season Grasses
Warm-season grasses flourish in warmer climates and have distinct nutrient needs.
- Slow-release nitrogen: Provides steady nutrition.
- Potassium-rich formulas: Improve heat tolerance.
| Grass Type | Fertilizer Type |
|---|---|
| Warm-season | Slow-release nitrogen, potassium-rich |
Turfgrass-specific Fertilizer Formulations
Certain fertilizers are specially formulated for specific types of turfgrass, ensuring optimal nutrition.
- Formulated blends: Tailored to meet the specific needs of various turfgrass species.
| Grass Type | Fertilizer Type |
|---|---|
| Turfgrass-specific | Tailored blends |
![calculating lawn fertilizer rates fact sheet Lawn Fertilizer Selection Criteria Calculating Lawn Fertilizer Rates [fact sheet]](https://extension.unh.edu/sites/default/files/migrated_unmanaged_files/Tableone.png)
Source Image: extension.unh.edu
Organic Fertilizer Options
Organic fertilizers are an eco-friendly choice, providing numerous benefits to your lawn and the environment.
Types of Organic Fertilizers
- Compost: Rich in nutrients, improves soil structure.
- Manure: Adds essential nutrients and organic matter.
- Bone Meal: High in phosphorus, supports root growth.
- Blood Meal: High in nitrogen, promotes green growth.
- Fish Emulsion: Balanced nutrients, quick absorption.
| Fertilizer Type | Source and Benefits |
|---|---|
| Compost | Nutrient-rich, improves soil structure |
| Manure | Adds essential nutrients and organic matter |
| Bone Meal | High in phosphorus, supports root growth |
| Blood Meal | High in nitrogen, promotes green growth |
| Fish Emulsion | Balanced nutrients, quick absorption |
Benefits of Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers offer several advantages over synthetic options.
- Environmentally friendly: Reduces chemical runoff.
- Improves soil health: Enhances soil structure and microbial activity.
- Safe for pets and children: Minimizes health risks.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmentally friendly | Reduces chemical runoff |
| Improves soil health | Enhances soil structure and microbial activity |
| Safe for pets and children | Minimizes health risks |
Application Techniques for Organic Fertilizers
Applying organic fertilizers correctly ensures maximum benefits.
- Even distribution: Use a spreader for uniform application.
- Watering in: Helps nutrients penetrate the soil.
- Timing: Apply during active growing periods.
| Technique | Importance |
|---|---|
| Even distribution | Ensures uniform application |
| Watering in | Helps nutrients penetrate the soil |
| Timing | Apply during active growing periods |

Source Image: www.pinterest.com
Synthetic Fertilizer Options
Synthetic fertilizers are widely used due to their immediate availability and effectiveness.
Advantages of Synthetic Fertilizers
- Quick results: Rapid nutrient absorption.
- Precise nutrient ratios: Tailored to specific needs.
- Cost-effective: Generally cheaper than organic options.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Quick results | Rapid nutrient absorption |
| Precise nutrient ratios | Tailored to specific needs |
| Cost-effective | Generally cheaper than organic options |
Potential Drawbacks
While effective, synthetic fertilizers come with some downsides.
- Environmental impact: Can cause chemical runoff.
- Soil health: May degrade soil structure over time.
- Over-application risk: Higher risk of burning grass.
| Drawback | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental impact | Can cause chemical runoff |
| Soil health | May degrade soil structure over time |
| Over-application risk | Higher risk of burning grass |
Best Practices for Application
Applying fertilizers correctly is crucial for their effectiveness and safety.
Proper Spreader Use
Using a spreader ensures even distribution of fertilizers.
- Calibrate spreader: Adjust settings for correct application rate.
- Overlap passes: Prevents missed spots.
| Practice | Importance |
|---|---|
| Calibrate spreader | Ensures correct application rate |
| Overlap passes | Prevents missed spots |
Calibration and Coverage
Calibrating your spreader ensures even and effective coverage.
- Check spreader settings: Follow manufacturer guidelines.
- Test application: Conduct a test run to ensure even distribution.
| Practice | Importance |
|---|---|
| Check spreader settings | Follow manufacturer guidelines |
| Test application | Ensures even distribution |
Timing and Frequency of Applications
Applying fertilizers at the right time and frequency is key to lawn health.
- Seasonal timing: Apply based on seasonal growth cycles.
- Regular intervals: Follow recommended application intervals.
| Practice | Importance |
|---|---|
| Seasonal timing | Apply based on growth cycles |
| Regular intervals | Follow recommended application intervals |
Source Image: www.myxxgirl.com
Lawn Fertilizer Selection Criteria
Specialty Fertilizers
Specialty fertilizers cater to specific lawn care needs, providing targeted benefits.
Weed and Feed Formulations
Weed and feed products combine fertilization with weed control.
- Nutrient-rich: Provides essential nutrients.
- Weed control: Kills and prevents weeds.
| Product Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Weed and Feed | Provides nutrients, controls weeds |
Disease and Pest Control Fertilizers
These fertilizers include ingredients to combat lawn diseases and pests.
- Nutrient-rich: Supports overall health.
- Pest control: Protects against insects and diseases.
| Product Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Disease and Pest Control | Supports health, protects against pests and diseases |
Fertilizers for High Traffic Areas
Special formulations strengthen lawns subjected to heavy foot traffic.
- Enhanced durability: Strengthens grass to withstand wear.
- Quick recovery: Promotes rapid regrowth.
| Product Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| High Traffic Area | Strengthens grass, promotes rapid regrowth |
Homemade and DIY Fertilizer Solutions
For those who prefer a more hands-on approach, homemade fertilizers can be effective and eco-friendly.
Simple DIY Fertilizer Recipes
Creating your own fertilizers can be easy and cost-effective.
- Compost tea: Nutrient-rich liquid from compost.
- Epsom salt mix: Provides magnesium and sulfur.
- Banana peel fertilizer: Adds potassium.
| Recipe | Ingredients and Benefits |
|---|---|
| Compost tea | Nutrient-rich liquid from compost |
| Epsom salt mix | Provides magnesium and sulfur |
| Banana peel fertilizer | Adds potassium |
Composting and Lawn Fertility
Composting is an excellent way to create a continuous supply of organic fertilizer.
- Kitchen scraps: Rich in nutrients.
- Garden waste: Adds essential organic matter.
| Compost Material | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Kitchen scraps | Rich in nutrients |
| Garden waste | Adds essential organic matter |
Using Grass Clippings and Mulch
Recycling grass clippings and using mulch can naturally fertilize your lawn.
- Grass clippings: Return nutrients to the soil.
- Mulch: Conserves moisture and improves soil structure.
| Material | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Grass clippings | Returns nutrients to the soil |
| Mulch | Conserves moisture, improves soil structure |

Source Image: duanpalmgarden.com
Fertilizer Safety and Storage
Proper handling and storage of fertilizers are essential for safety and effectiveness.
Safe Handling Practices
Follow these practices to ensure safe fertilizer use.
- Wear gloves: Protects skin from chemicals.
- Wash hands: Prevents ingestion of chemicals.
- Store safely: Keep out of reach of children and pets.
| Practice | Importance |
|---|---|
| Wear gloves | Protects skin from chemicals |
| Wash hands | Prevents ingestion of chemicals |
| Store safely | Keeps out of reach of children and pets |
Proper Storage Conditions
Storing fertilizers correctly maintains their effectiveness.
- Dry location: Prevents moisture damage.
- Cool temperature: Avoids heat degradation.
- Sealed containers: Keeps products fresh.
| Storage Condition | Importance |
|---|---|
| Dry location | Prevents moisture damage |
| Cool temperature | Avoids heat degradation |
| Sealed containers | Keeps products fresh |
Disposal of Unused Fertilizers
Dispose of unused fertilizers responsibly to protect the environment.
- Follow local regulations: Adhere to disposal guidelines.
- Avoid waterways: Prevent contamination of water sources.
| Disposal Practice | Importance |
|---|---|
| Follow local regulations | Adhere to disposal guidelines |
| Avoid waterways | Prevent contamination of water sources |
Evaluating Fertilizer Effectiveness
Monitoring your lawn’s health and adjusting fertilization strategies ensures long-term success.
Monitoring Lawn Health
Regularly check your lawn for signs of health or distress.
- Color: Vibrant green indicates good health.
- Growth rate: Consistent growth suggests proper nutrition.
- Pest presence: Look for signs of insect or disease issues.
| Indicator | Significance |
|---|---|
| Color | Vibrant green indicates good health |
| Growth rate | Consistent growth suggests proper nutrition |
| Pest presence | Signs of insect or disease issues |
Adjusting Fertilization Strategies
Fine-tune your fertilization plan based on observed results.
- Increase or decrease nutrients: Based on lawn response.
- Change fertilizer type: If current type isn’t effective.
| Adjustment | Reason |
|---|---|
| Increase/decrease nutrients | Based on lawn response |
| Change fertilizer type | If current type isn’t effective |
Long-term Lawn Care Plans
Develop a comprehensive plan for year-round lawn care.
- Seasonal fertilization: Adjust based on seasonal needs.
- Regular maintenance: Mowing, watering, and aerating.
| Plan Element | Importance |
|---|---|
| Seasonal fertilization | Adjust based on seasonal needs |
| Regular maintenance | Mowing, watering, and aerating |
By understanding and applying these principles of lawn fertilization, you’ll be well on your way to achieving a beautiful, healthy lawn that you can be proud of. Happy gardening!

