Have you ever wondered how to multiply your garden plants effortlessly? Rhizome division is your secret weapon. This propagation method harnesses the natural growth habits of certain plants, allowing gardeners to increase their plant population without the need for seeds. It’s not only fascinating but also a highly effective way to ensure your garden thrives year after year.
Benefits of Rhizome Division: Increasing Plant Population and Vigor
Why should you consider rhizome division? Here are some compelling reasons:
- Boost Plant Numbers: Quickly increase the number of plants in your garden.
- Enhance Plant Health: Dividing rhizomes can rejuvenate older plants.
- Cost-Effective: Save money by propagating your own plants instead of buying new ones.
- Preserve Plant Varieties: Maintain and share beloved plant species.
- Improve Garden Design: Easily fill gaps in your garden with new plants.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Boost Plant Numbers | Multiply your plant collection quickly and efficiently. |
| Enhance Plant Health | Divided rhizomes lead to healthier, more vigorous plants. |
| Cost-Effective | Save money by propagating plants instead of purchasing new ones. |
| Preserve Plant Varieties | Keep and share unique or favorite plant species. |
| Improve Garden Design | Fill garden gaps and create balanced designs effortlessly. |
Source Image: propg.ifas.ufl.edu
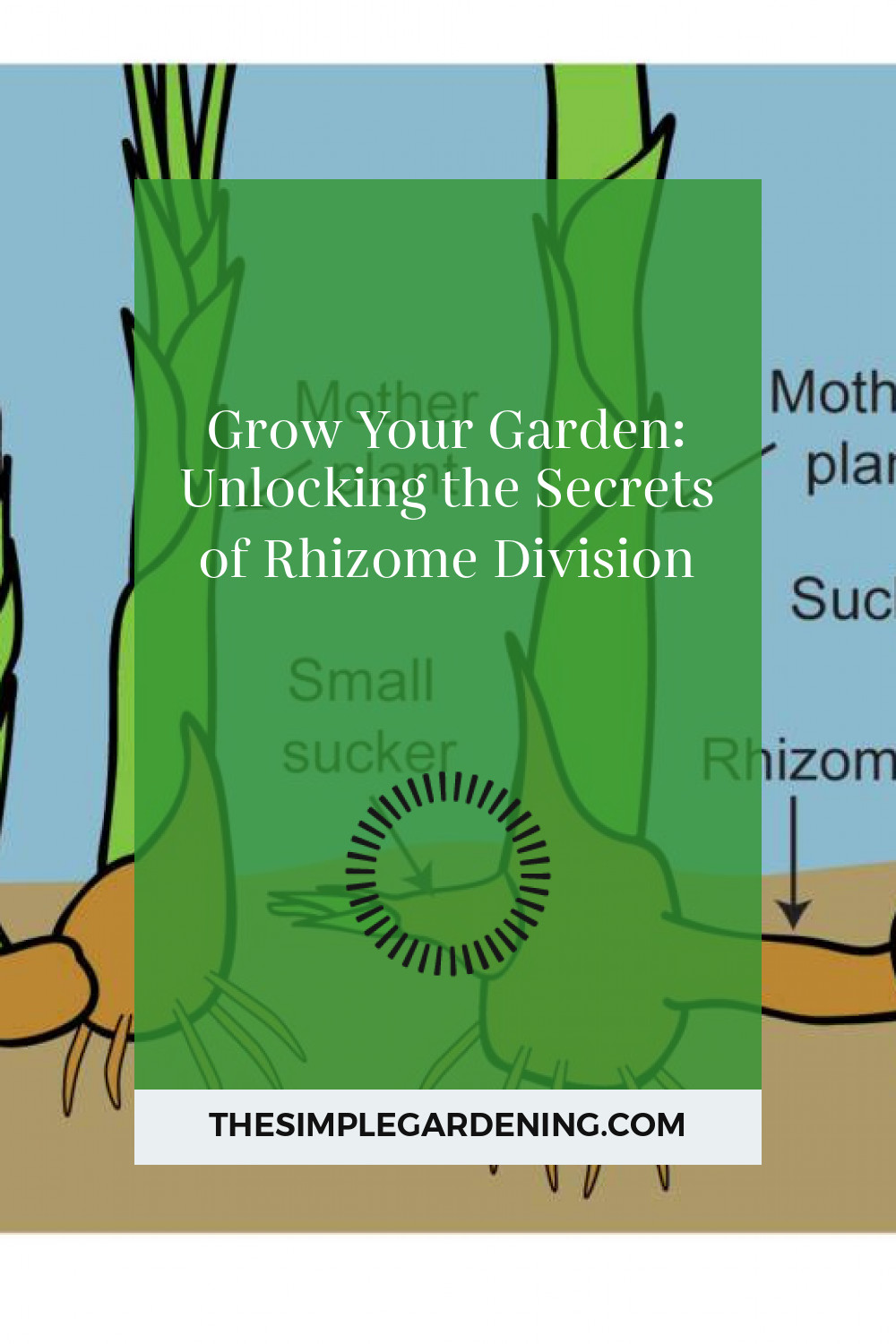
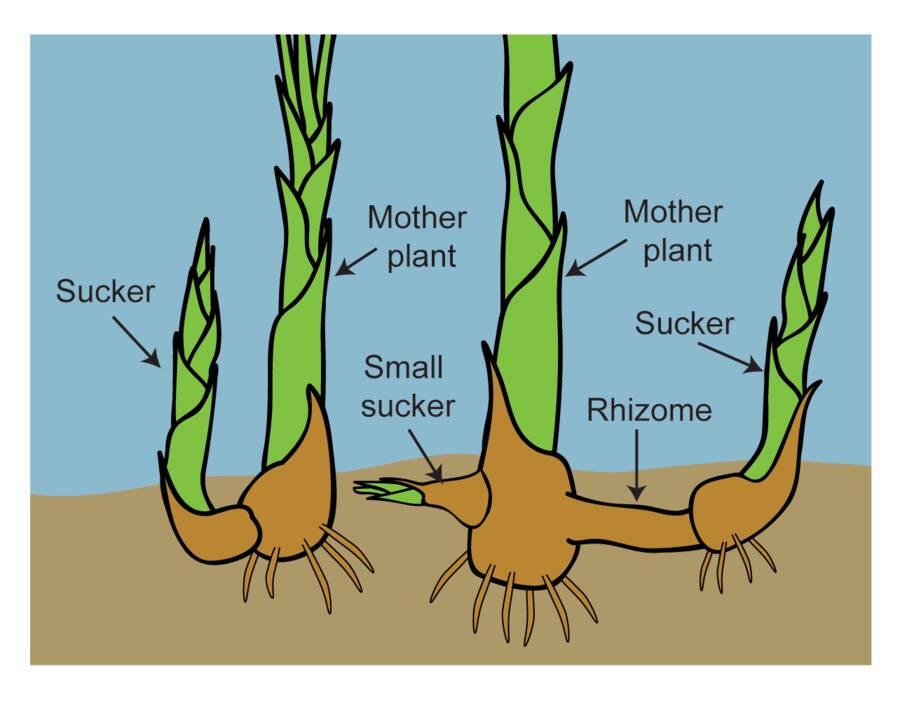
Understanding Rhizomes
What Are Rhizomes? Exploring Their Structure and Function
Rhizomes are underground plant stems that grow horizontally, producing roots and shoots from their nodes. Unlike regular roots, rhizomes store nutrients, making them essential for plant survival and propagation. They enable plants to spread and colonize new areas, ensuring growth and survival even in challenging conditions.
Common Plants Propagated by Rhizome Division
Several plants are ideal candidates for rhizome division, including:
- Irises
- Bamboo
- Ginger
- Canna lilies
- Turf grasses
| Plant | Notable Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Irises | Beautiful, colorful blooms. |
| Bamboo | Fast-growing and hardy. |
| Ginger | Edible rhizomes with medicinal properties. |
| Canna lilies | Vibrant flowers and tropical foliage. |
| Turf grasses | Essential for lawns and ground cover. |
Timing and Preparation
Best Time to Divide Rhizomes: Seasonal Considerations
The timing of rhizome division is crucial for success. Generally, the best times are early spring or late fall. During these periods, plants are either just starting to grow or winding down for the season, making them less stressed by the division process.
Preparing Plants for Rhizome Division: Tools and Techniques
Preparation is key. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Clean, sharp tools: Spades, knives, or pruning shears.
- Disinfectant: To prevent disease spread.
- Water: To hydrate plants before and after division.
- Compost or organic matter: To enrich the soil post-division.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Spades, Knives, Pruning Shears | For clean, precise cuts. |
| Disinfectant | Prevents disease transmission. |
| Water | Keeps plants hydrated and reduces stress. |
| Compost or Organic Matter | Enhances soil fertility and plant growth. |
Source Image: stock.adobe.com
Division Techniques
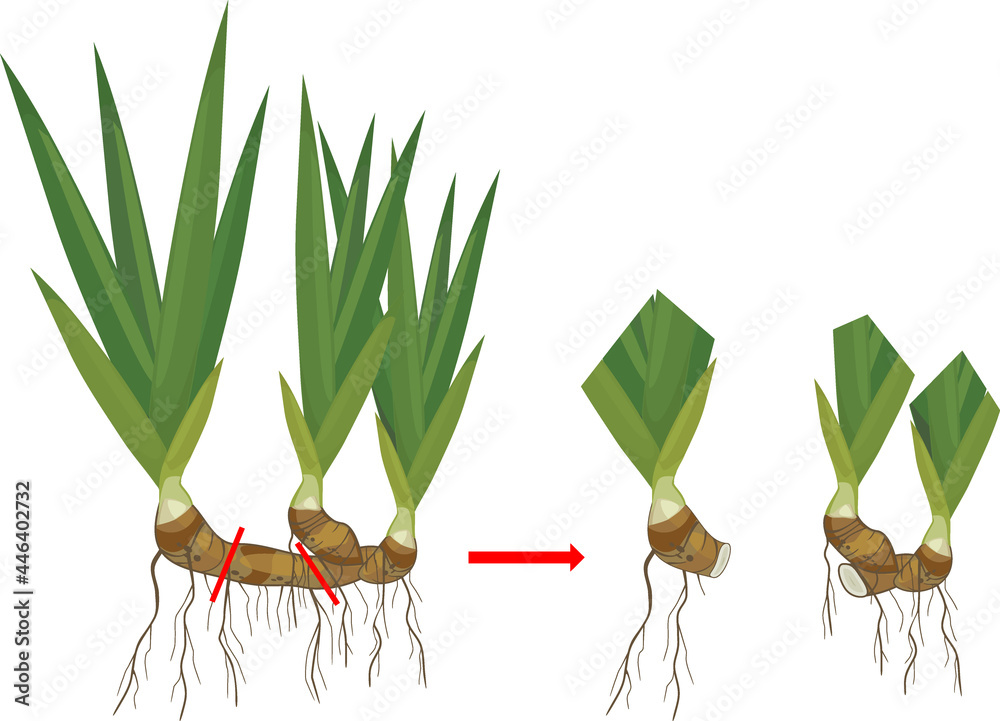
Step-by-Step Guide to Dividing Rhizomes
Follow these steps for successful rhizome division:
- Water the plant thoroughly a day before division.
- Dig up the plant carefully to avoid damaging the rhizomes.
- Clean the rhizomes by removing soil and old foliage.
- Cut the rhizomes into sections, ensuring each has at least one bud.
- Disinfect the cuts with a fungicide to prevent rot.
- Replant the divisions at the same depth they were originally growing.
Division Methods for Different Types of Rhizomatous Plants
Different plants may require slightly varied techniques:
- Irises: Divide every 3-4 years, discarding old central sections.
- Bamboo: Use a sharp spade to separate sections.
- Ginger: Ensure each piece has at least one “eye” or bud.
- Turf grasses: Slice into manageable sections for replanting.
| Plant | Division Technique |
|---|---|
| Irises | Divide every 3-4 years, discard old centers. |
| Bamboo | Use a spade to separate sections. |
| Ginger | Ensure each section has a bud or “eye”. |
| Turf grasses | Slice into sections for replanting. |
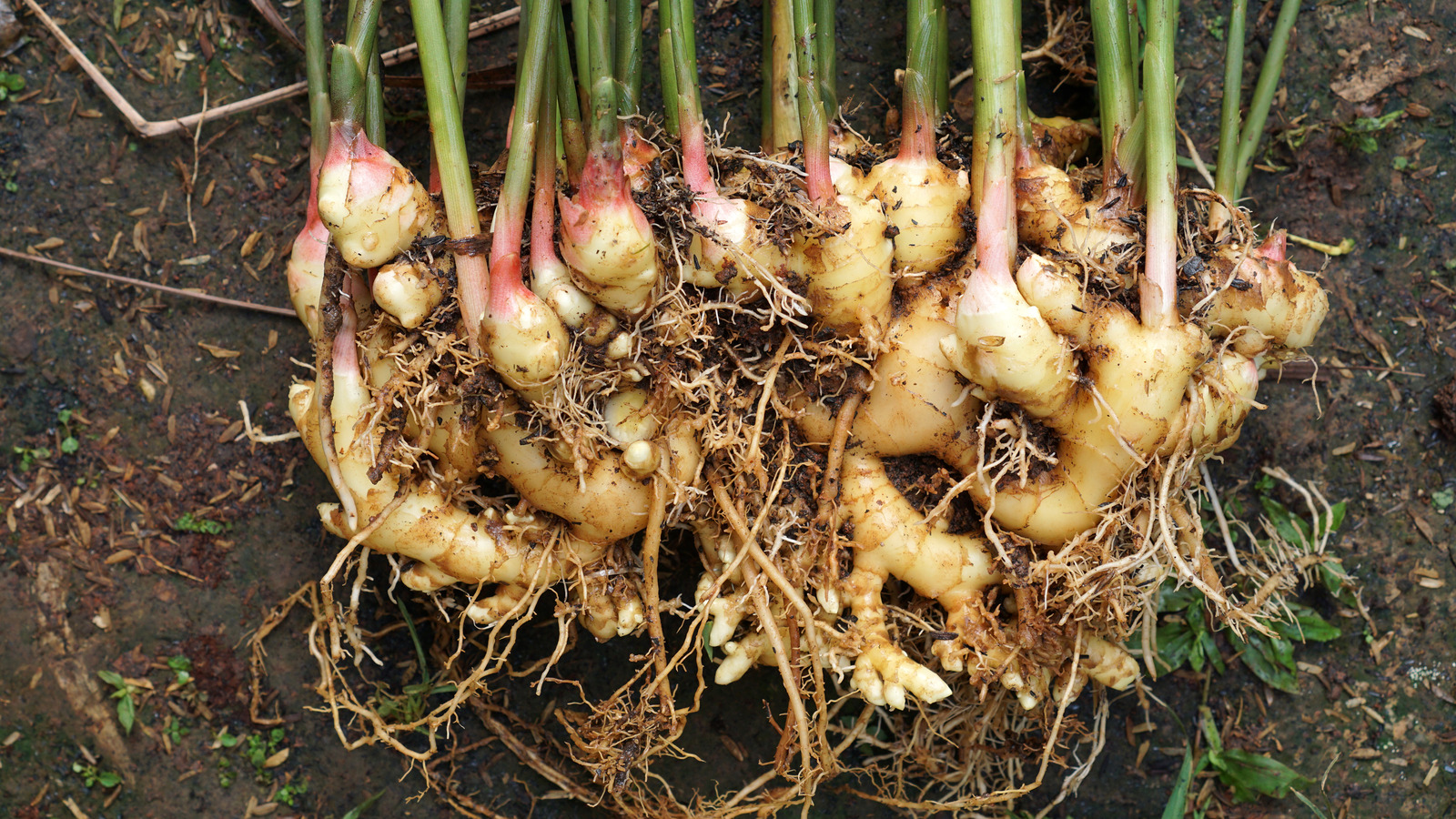

Source Image: www.housedigest.com
Plant Selection
Choosing Plants Suitable for Rhizome Division
Selecting the right plants is essential. Look for:
- Healthy, vigorous growth.
- Visible, healthy rhizomes.
- Plants that are not too young or old.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Rhizomatous Species
Consider these factors:
- Climate compatibility: Choose plants suited to your climate.
- Soil requirements: Match plants to your soil type.
- Space: Ensure you have enough space for spreading plants.
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Climate Compatibility | Choose plants suited to local climate conditions. |
| Soil Requirements | Match plants to your soil type for optimal growth. |
| Space | Ensure sufficient space for plant spread. |
Division Depth and Size
Determining the Optimal Depth and Size for Rhizome Division
The right depth and size are crucial:
- Depth: Plant divisions at the same depth as the original plant.
- Size: Each division should have at least one healthy bud and a portion of the root system.
Tips for Dividing Rhizomes Without Damaging Plants
- Use sharp, clean tools to make precise cuts.
- Avoid cutting too small to ensure each section has enough resources.
- Handle gently to prevent breakage.
| Consideration | Tip |
|---|---|
| Depth | Plant at the original depth. |
| Size | Ensure each section has a bud and roots. |
| Tool Sharpness | Use sharp tools for clean cuts. |
| Handling | Handle gently to avoid damage. |
![divide and store iris rhizomes Rhizome Division How To Divide And Store Iris Rhizomes [For Planting Next Season]](https://gardentabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Exposed-Iris-Rhizomes-or-Roots.jpg)
Source Image: gardentabs.com
Transplanting
Transplanting Divided Rhizomes: Tips for Success
After division, follow these steps for successful transplanting:
- Prepare the soil: Enrich with compost or organic matter.
- Plant divisions: Place them at the correct depth.
- Water well: Ensure the soil is moist but not waterlogged.
- Mulch: Helps retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Soil and Watering Requirements After Transplanting
Post-transplant care is vital:
- Soil: Well-draining, rich in organic matter.
- Watering: Keep soil consistently moist until established.
| Step | Detail |
|---|---|
| Soil Preparation | Enrich with compost or organic matter. |
| Planting Depth | Place divisions at the original depth. |
| Watering | Keep soil moist, avoid waterlogging. |
| Mulching | Retains moisture, suppresses weeds. |
Propagation Containers
Choosing Containers for Rhizome Division
For those dividing rhizomes indoors or in limited spaces:
- Choose large, deep pots to accommodate growth.
- Ensure good drainage to prevent waterlogging.
- Use high-quality potting mix rich in nutrients.
Ideal Growing Conditions for Newly Divided Rhizomes
Provide optimal conditions:
- Light: Bright, indirect sunlight.
- Temperature: Maintain moderate temperatures, avoid extremes.
- Humidity: Keep moderate to high, especially for tropical plants.
| Condition | Ideal Specification |
|---|---|
| Container Size | Large, deep pots. |
| Drainage | Ensure good drainage. |
| Potting Mix | Rich in nutrients. |
| Light | Bright, indirect sunlight. |
| Temperature | Moderate, avoid extremes. |
| Humidity | Moderate to high. |
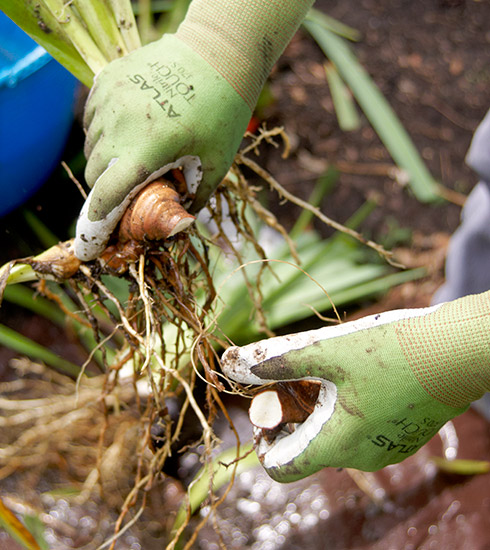

Source Image: gardengatemagazine.com
Managing Growth
Managing Rhizome Growth: Preventing Overcrowding
Overcrowding can hinder growth. Here’s how to manage it:
- Regular division: Every few years, divide plants to control spread.
- Thinning: Remove excess growth to allow air circulation.
- Spacing: Ensure sufficient space between plants when replanting.
Pruning and Thinning Techniques for Healthy Rhizomatous Plants
Pruning and thinning are essential:
- Prune dead or damaged foliage regularly.
- Thin out dense growth to improve air circulation.
- Monitor for pests and diseases and address promptly.
| Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Regular Division | Controls spread, prevents overcrowding. |
| Thinning | Improves air circulation, reduces competition. |
| Pruning | Removes dead/damaged foliage, maintains health. |
Maintenance and Care
Caring for Divided Rhizomes: Watering, Fertilizing, and Pest Control
Proper care ensures thriving plants:
- Watering: Keep soil moist but not waterlogged.
- Fertilizing: Use balanced, slow-release fertilizers.
- Pest control: Monitor for pests and use organic treatments if needed.
Monitoring Plant Health After Division
Regular monitoring is crucial:
- Inspect regularly for signs of stress or disease.
- Adjust care based on plant response.
- Support new growth with stakes if necessary.
| Care Aspect | Tip |
|---|---|
| Watering | Keep soil moist, avoid waterlogging. |
| Fertilizing | Use balanced, slow-release fertilizers. |
| Pest Control | Monitor and treat organically. |
| Monitoring | Regularly inspect and adjust care. |
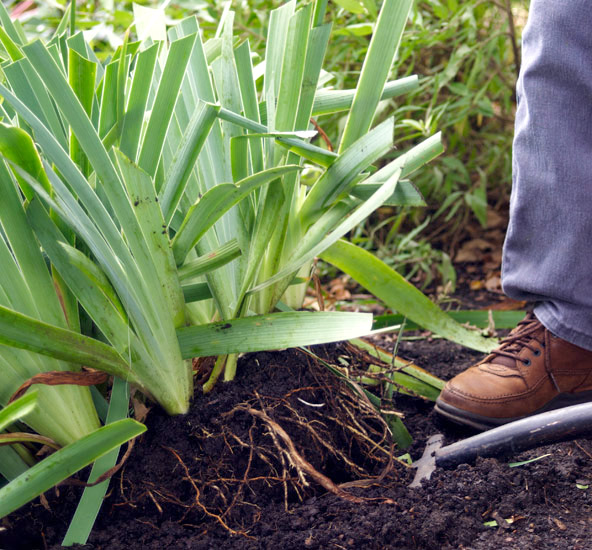

Source Image: gardengatemagazine.com
Rhizome Division
Propagation Success
Signs of Successful Rhizome Division: Root Development and Growth
Successful division shows these signs:
- New shoots emerging from the soil.
- Healthy root development visible on inspection.
- Vigorous growth and expansion of the plant.
Troubleshooting Common Issues After Rhizome Division
Common problems and solutions:
- Slow growth: Ensure proper watering and soil conditions.
- Wilting: Check for pests, water stress, or disease.
- No new shoots: Re-evaluate planting depth and environmental conditions.
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Slow Growth | Ensure proper watering and soil conditions. |
| Wilting | Check for pests, water stress, or disease. |
| No New Shoots | Re-evaluate planting depth and conditions. |
Companion Planting
Companion Plants for Rhizomatous Species
Enhance your garden with companion plants:
- Marigolds: Repel pests and attract beneficial insects.
- Lavender: Adds fragrance and deters pests.
- Chives: Improve soil health and deter insects.
Enhancing Garden Design with Rhizome Division and Companion Planting
Companion planting can:
- Improve plant health by deterring pests.
- Enhance aesthetics with varied textures and colors.
- Support pollinators by providing diverse flowering plants.
| Companion Plant | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Marigolds | Repel pests, attract beneficial insects. |
| Lavender | Adds fragrance, deters pests. |
| Chives | Improve soil health, deter insects. |

Source Image: biologydictionary.net
Naturalizing Landscapes
Using Rhizome Division to Naturalize Outdoor Spaces
Naturalizing creates low-maintenance landscapes:
- Select native plants for your area.
- Allow plants to spread naturally for a more organic look.
- Minimal intervention: Let nature take its course.
Creating Low-Maintenance Gardens with Rhizomatous Plants
Advantages include:
- Reduced upkeep: Less weeding and watering.
- Sustainable: Supports local ecosystems.
- Attractive year-round: Provides seasonal interest.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reduced Upkeep | Less weeding and watering. |
| Sustainable | Supports local ecosystems. |
| Year-Round Interest | Provides seasonal beauty. |
Indoor Gardening
Growing Rhizomatous Plants Indoors: Tips and Considerations
Bring rhizomatous plants indoors with these tips:
- Light: Ensure ample indirect sunlight.
- Humidity: Maintain higher humidity levels.
- Space: Provide room for growth and spread.
Designing Indoor Spaces with Divided Rhizomes in Mind
Consider:
- Containers: Use stylish pots that complement your decor.
- Arrangement: Group plants for a lush, green display.
- Maintenance: Regularly check for pests and adjust care as needed.
| Consideration | Tip |
|---|---|
| Light | Ensure ample indirect sunlight. |
| Humidity | Maintain higher humidity levels. |
| Containers | Choose stylish, complementary pots. |
| Arrangement | Group plants for a lush display. |
Sharing Plants
Sharing the Bounty: Propagating Plants Through Rhizome Division
Share your garden’s bounty by:
- Hosting plant swaps: Exchange divided plants with friends.
- Donating to community gardens: Support local green spaces.
- Organizing workshops: Teach others about rhizome division.
Community Plant Swaps and Rhizome Division Workshops
Benefits include:
- Building community: Connect with fellow gardeners.
- Learning opportunities: Share and gain knowledge.
- Expanding plant variety: Access diverse plant species.
| Activity | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Plant Swaps | Exchange plants, build community. |
| Donations | Support local gardens, enhance green spaces. |
| Workshops | Share knowledge, learn new techniques. |
Harnessing the Power of Rhizome Division for Plant Propagation
Rhizome division is a gardener’s best friend, offering an easy, effective way to propagate plants, enhance garden design, and share the joy of gardening with others. By mastering this technique, you can ensure a vibrant, thriving garden that brings joy and beauty to your outdoor spaces year after year.
Empowering Gardeners to Expand Their Gardens Through Successful Division Practices
Embrace rhizome division and watch your garden flourish. With the right techniques and a bit of practice, you’ll become proficient in this rewarding method, enjoying the benefits of healthier plants, increased plant diversity, and the satisfaction of growing your garden through your own efforts.